Silk and Silk Worms
Silk and Silk Worms – The Caterpillar, Cocoon, Chrysalis, Moth
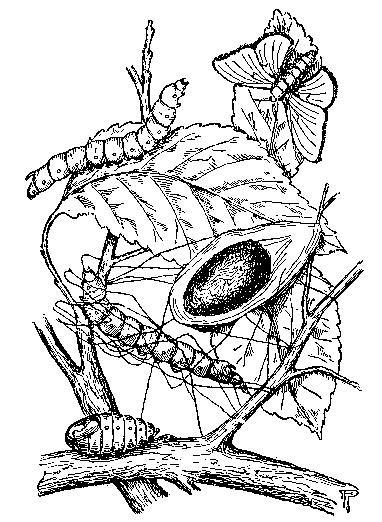
Image and text from Textiles and Clothing by Kate Heintz Watson. American School of Home Economics, 1907.About the Silk Worm and How Silk Is Created
The silk of commerce begins with an egg no bigger than a mustard seed, out of which comes a diminutive caterpillar, which is kept in a frame and fed upon mulberry leaves. When the caterpillars are full grown, they climb upon twigs placed for them and begin to spin or make the cocoon. The silk comes from two little orifices in the head in the form of a glutinous gum which hardens into a fine elastic fiber. With a motion of the head somewhat like the figure eight, the silk worm throws this thread around the body from head to tail until at last it is entirely enveloped. The body grows smaller and the thread grows finer until at last it has spun out most of the substance of the body and the task is done.If left to itself, when the time came, the moth would eat its way out of the cocoon and ruin the fiber. A few of the best cocoons are saved for a new supply of caterpillars; the remainder are baked at a low heat which destroys the worm but preserves the silk. This now becomes the cocoon of commerce.
Next the cocoons go to the reelers who wind the filaments into the silk yarn that makes the raw material of our mills. The cocoons are thrown into warm water mixed with soap in order to dissolve the gum. The outer or coarser covering is brushed off down to the real silk and the end of the thread found. Four or five cocoons are wound together, the sticky fibers clinging to each other as they pass through the various guides and are wound as a single thread on the reels. The silk is dried and tied into hanks or skeins. As the thread unwinds from the cocoon, it becomes smaller, so other threads must be added.
At the mill the raw silk goes to the “throwster” who twists the silk threads ready for the loom. These threads are of two kinds—”organize” or warp and “tram” or filling. The warp runs the long way of woven fabric or parallel with the selvage and it must be strong, elastic, and not easily parted by rubbing. To prepare the warp, two threads of raw silk are slightly twisted. Twist is always put into yarn of any kind to increase its strength. These threads are united and twisted together and this makes a strong thread capable of withstanding any reasonable strain in the loom and it will not roughen. For the woof or tram which is carried across the woven cloth on the shuttle, the thread should be as loose and fluffy as possible. Several threads are put together, subjected to only a very slight twist—just enough to hold the threads together so they will lie evenly in the finished fabric.
After the yarn leaves the spinners it is again run off on reels to be taken to the dye house. First the yarn is boiled off in soapy water to remove the remaining gum. Now the silk takes on its luster. Before it was dull like cotton. The silk is now finer and harder and is known as “souple.”
The silk fiber has a remarkable property of absorbing certain metallic salts, still retaining much of its luster. This process is known as “loading” or “weighting,” and gives increased body and weight to the silk. Silk without weighting is known as “pure dye,” of which there is little made, as such goods take too much silk.
Renee Shelton.

Comments
Post a Comment